What is Camel K
Camel K is a Kubernetes Operator in charge to manage the lifecycle of Camel workloads running on the cloud. It can manages aspects like build and deploy (managed Integrations), only deploy (self managed build Integrations) and any other operational aspects (promoting across environments, monitoring, resource tuning, upgrades, interactions with Knative and Kafka, …).
Integrations
A Camel workload is generally represented by a route expressed in any Camel DSL. This is wrapped into one or more custom resource which will manage the lifecycle of the application on the cloud.
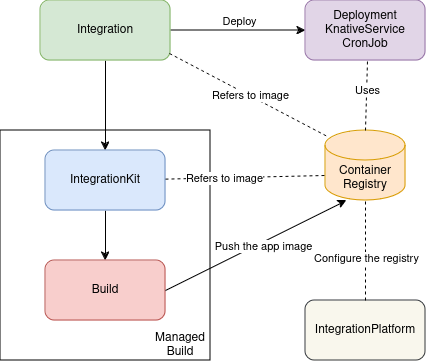
The user is responsible to create a single IntegrationPlatform which contains the configuration required to drive the build and publishing process. Then the user creates any Integration custom resource, which is mainly a container for the Camel route and other optional Kubernetes fine tunings.
IntegrationPlatform: it is required to configure building aspects such as which container registry to use or Maven configuration settings.
Integration: it is used to create the Camel application, setting mainly the Camel route the user wants to run on the cloud. The user can provide a self managed build Integration as well, in which case, the operator will skip the building part.
IntegrationKit: the operator will reuse an existing IntegrationKit if the Integration has the same set of capabilities and dependencies. Otherwise it creates an IntegrationKit with the configuration required by the Integration. The presence of this resource makes Camel K applications to run immediately, when reusing an existing IntegrationKit.
Build: the operator will create a Build for each IntegrationKit. It creates a Maven project with the dependencies required by the IntegrationKit, it builds and it publish to a given registry.
Deployment, KnativeService, CronJob: the operator will create any of those deployment objects to run the Camel application. The default choice is the Deployment resource, unless the operator detects the Camel route is more suitable to run as a CronJob (ie, when there is a scheduler component such as Quartz). If the Camel route contains an HTTP service and the cluster provides a Knative installation, then, a KnativeService is used instead as a deployment.
Pipes (Connectors)
The user can use an alternative approach using the Pipe (Connector) abstraction. With Pipe, he can provide a declarative connector-style approach, connecting an Event Source to an Event Sink. The source and sink can be any Kubernetes object reference that the operator can transform. The operator will be in charge to transform such a Pipe into an Integration and start the build and deployment process as described above.
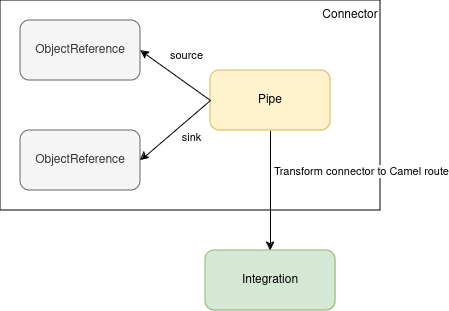
Pipe: it is used to create the connector binding an event source to an event sink.
ObjectReference: this is the reference to any Kubernetes object. The operator is able to transform any Camel URI, Kamelet, Strimzi Kafka resource, Knative resource, Service, Integration or Pipe.
Integration: it is created from the Pipe translating the source and sinks into a Camel route.